ENDODONTICS
RCT (Root Canal Treatment)
This procedure is performed to protect a badly decayed or infected tooth by removing the center part (pulp) of the tooth. Dental pulp contains nerves, blood vessel and other connective tissue which helps in growth of the root of the tooth.
Indications
Following are the indications for root canal treatment:
- Painful tooth
- Prolonged sensitivity
- Decayed tooth
- Discoloration of tooth
- Non-vital tooth
Procedure
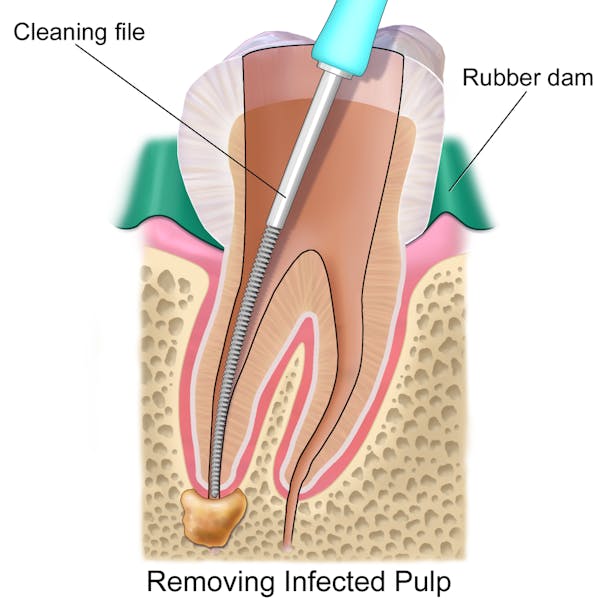
Root canal treatment takes place in single or multiple sittings. Dentist begins the procedure by taking an X-ray; this is done to determine the shape of the root canal. Then, local anesthesia is administered to numb the tooth. After the tooth becomes numb; an opening is made on the surface of the tooth to access the pulp chamber. Using special files, pulp along with bacteria and related debris is removed from the tooth and the root canals are disinfected with the help of disinfectants. Next, a series of files of increasing diameter are use to shape the canals so that they can be filled with root canal fillings known as gutta percha. During this process canals are properly irrigated with water or sodium hypochlorite to flush away the debris. Gutta percha is a thermoplastic material which is heated and then compressed into and against the walls of the root canals to seal them. Sealing of canal is important to prevent them from becoming reinfected with bacteria.
Final step involves permanent restoration of tooth, to replace lost tooth structure and to prevent it from breaking. It could be either restoration or crown. At times, a post (metal or strong plastic) is inserted into the canal to give crown more support. Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection.
Aftercare
Taking proper care of the tooth and mouth post-surgery will aid in the healing time and discomfort.
- Avoid hard foods for few days after the treatment.
- Regular brushing and flossing is important.
- It is advisable to avoid food or drink for two to three hours after the procedure.
- After root canal treatment, tooth becomes weak and brittle. To increase the strength of the tooth, dental crown is advised.
Side effects
The possible side effects of a root canal procedure can be the following:
- A dull to sharp pain might be experienced following the procedure.
- In some cases the tooth becomes darker, which can be treated by artificial crown.
- Swelling around the treated tooth is very common.
- Patient may feel sensation or discomfort.
Pulp Capping
Pulp capping is done to prevent the dental pulp from necrosis after being exposed. It is of 2 types:
- Direct pulp capping
- Indirect pulp capping
Direct pulp capping
This procedure is performed to protect exposed vital pulp by placing dental material directly over the pulp. It is usually performed when there is minimal pulp exposure and is asymptomatic.
Procedure
First, radiograph is taken to confirm whether direct pulp capping is sufficient or not. The tooth is then anesthetized and isolated with rubber dam. If etiology was any carious lesion then caries is removed and sodium hypochlorite dressing is placed for 10 minutes to achieve hemostasis. Finally, a filling or another type of restoration is placed on the tooth.
Indirect pulp capping
This procedure is performed when pulp tissue is close to the surface but not actually exposed. The deepest layer of the remaining affected dentin is covered with a layer of biocompatible material in order to prevent pulp exposure and further trauma to the pulp.
Procedure
In case of indirect pulp capping, the procedure is carried out in two or more sittings. Tooth is anesthetized and isolated with rubber dam. All the caries except that immediately over the pulp is removed. The remaining thin layer of caries is covered with a biocompatible material and sealed with a restoration for a period of 6-8 weeks. In next visit, temporary material is removed and the remaining caries is excavated. At last, the tooth is given a permanent restoration.
Material used for pulp capping
Some of the commonly used materials for pulp capping are:
- Calcium hydroxide
- MTA(mineral trioxide aggregate)
- Tri-calcium phosphate
- ZOE (zinc oxide eugenol)
- Calcium phosphate ceramic
Success rate
The outcome of the treatment procedure largely depends on the condition of the tooth and the material used. However, the success rate of pulp capping is very high.
DISCLAIMER
This web page provides general information and discussions about health, medicine and related subjects. The information and other content provided on this website, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment.
The content is for information purpose only and is not a medical advice. Qualified doctors have gathered information from reputable sources; however Credence Medicure Corporation is not responsible for errors or omissions in reporting or explanations. No individual should use the information, resources and tools contained herein to self diagnose or self treat any medical condition.
If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your health care provider or seek other professional medical treatment. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something that have read on this blog or in any linked materials. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately.
The opinions and views expressed on this blog and website have no relation to those of any academic, hospital, health practice or other institution. Credence Medicure Corporation gives no assurance or warranty regarding the accuracy, timeliness or applicability of the content.