Cushing’s syndrome
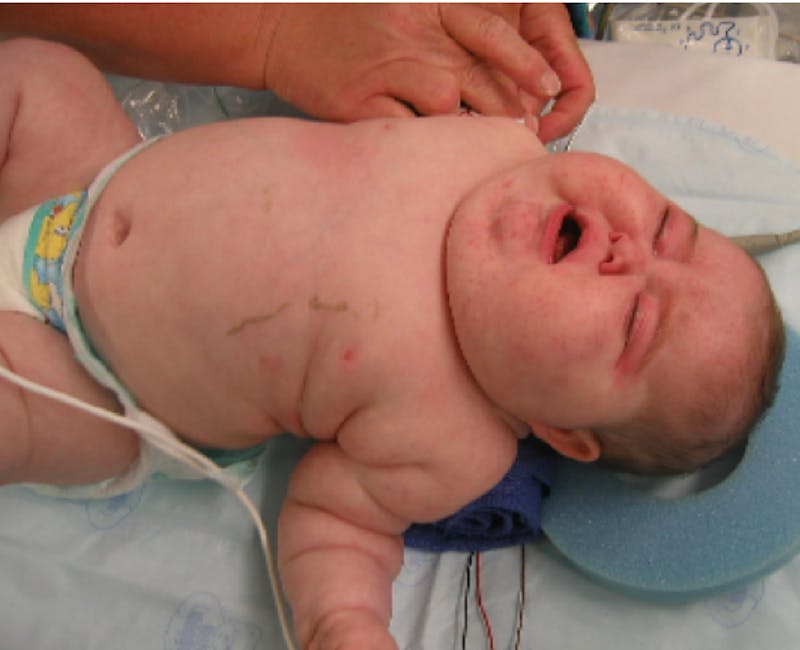
Cushing’s syndrome, also known as hypercortisolism, is a rare disorder that occurs when the body is exposed to too much of the hormone cortisol. Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Adrenal glands are stimulated by a pituitary hormone (ACTH) to produce cortisol, which is essential for many bodily functions. It helps the body manage stress, inhibit inflammation, and regulate blood sugar.
What causes Cushing’s syndrome?
- Steroid medicine: Many people develop Cushing syndrome because of overuse of steroid medicines such as prednisone to treat another medical condition such as chronic asthma, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases.
- Tumor of the pituitary gland: Another main cause of Cushing’s syndrome is a tumor of the pituitary gland. This condition is known as Cushing’s disease. It occurs when excess ACTH production from pituitary tumor causes adrenal glands to produce too much cortisol.
- Tumor of adrenal glands: The overproduction of cortisol could be triggered by a tumor of the adrenal glands. It could be one adrenal gland producing excess cortisol or both.
Tumor in another part such as the lung tumor may produce ACTH, which in turn stimulate adrenal glands to produce excess corticosteroids.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome vary and often appear gradually. These may include:
- Weight gain, especially around the abdomen, and may be particularly noticeable at the top of the back (called a buffalo hump).
- The arms and legs remain slender.
- Changes in the skin, including easy bruising, skin thinning, and striae that look like stretch marks may develop over the abdomen and chest.
- Round and puffy face, commonly known as moon face
- Irregular menstrual periods and excessive body hair in women.
- Men may experience a decrease in fertility
- Muscular weakness
- High blood pressure
- High blood sugar
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made based upon thorough medical history and physical examinations. It is very difficult to diagnose because the symptoms of Cushing’s can be very wide ranging. Your doctor will ask you about your past health and may ask you to get a blood test and a urine test. Cushing syndrome can be diagnosed by measuring levels of cortisol in the urine, blood or saliva.
24 hour urine test
You may be asked to collect your urine for 24 hours, this is used to evaluate the level of cortisol.
Dexamethasone suppression screening test
This evaluates the response of body to large doses of artificial steroid. It is used to distinguish Cushing syndrome from other causes of excess cortisol. It tells, whether the excess production of corticotrophins (ACTH) is due to the pituitary gland, or tumor elsewhere. In people, who do not have Cushing, dexamathasone should decrease their level of cortisol.
CT scan or MRI
These are done to look for a tumor on your adrenal glands and pituitary gland.
Treatment
The treatment depends upon the cause and may include surgery, cortisol- inhibiting drugs, radiotherapy or chemotherapy. If long term use of steroid medicine is the cause, then your doctor will gradually lower your dose over time. Do not stop taking these medicines without your doctor’s approval. This can be very dangerous.
For patients with Cushing disease, surgery to remove the pituitary tumor offers the best chance for recovery. Surgery reduces the ACTH secretion, allowing the pituitary to return to normal functions. Sometimes, radiation is needed as well. When surgery is not successful, treatment with medications may be attempted.
If the Cushing syndrome is caused by an adrenal tumor, then surgery to remove the tumor is recommended. It is done only if the tumor is not cancerous. If the tumor is cancerous, then the whole adrenal gland is removed.
Tumors in the lungs or other organs are treated with surgery, radiation or chemotherapy.
DISCLAIMER
This web page provides general information and discussions about health, medicine and related subjects. The information and other content provided on this website, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment.
The content is for information purpose only and is not a medical advice. Qualified doctors have gathered information from reputable sources; however Credence Medicure Corporation is not responsible for errors or omissions in reporting or explanations. No individual should use the information, resources and tools contained herein to self diagnose or self treat any medical condition.
If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your health care provider or seek other professional medical treatment. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something that have read on this blog or in any linked materials. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately.
The opinions and views expressed on this blog and website have no relation to those of any academic, hospital, health practice or other institution. Credence Medicure Corporation gives no assurance or warranty regarding the accuracy, timeliness or applicability of the content.
