Pneumonia
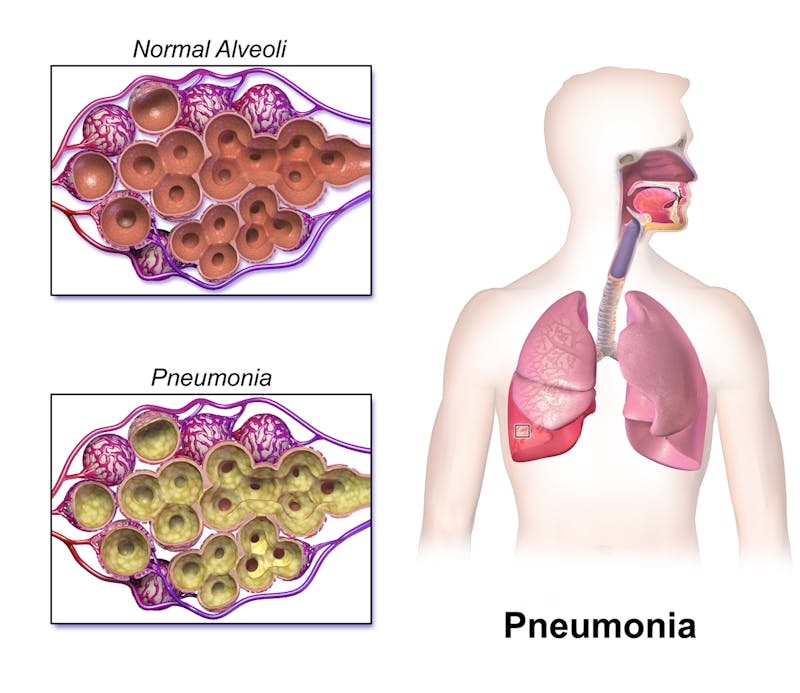
Pneumonia is an inflammation of tissue in one or both of the lungs, caused by a bacteria, virus, or fungi. This infection causes the air sacs of your lungs to fill up with fluid or pus, resulting in symptoms such as cough with phlegm, fever, chills and trouble breathing. It is a life threatening disease and can affect people of any age.
Symptoms of pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia depend upon various factors, such as, age of person, cause of infection or severity of infection. The common symptoms of pneumonia include:
- Cough
- Fever
- Difficulty breathing
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Sweating
- Chest pain
- Haemoptysis (blood during cough)
- Loss of appetite
Cause of Pneumonia
There are many different causes of pneumonia. Most often it occurs due to bacteria or virus. It can transfer from person to person through direct contact or by inhaling droplets in the air from coughing and sneezing. It can also be triggered by a cold or flu. The main types of pneumonia are:
Bacterial pneumonia
The pneumonia caused by bacteria is the most common cause of pneumonia in adults. It can occur suddenly with a high fever, coughing and fast breathing. There are many different types of bacteria that can cause pneumonia. The most common type of bacteria responsible for bacterial pneumonia is streptococcus pneumoniae.
Viral Pneumonia
Viral Pneumonia is a common cause of pneumonia in young children. It usually lasts for a shorter duration and can be caused by any virus including adenovirus, influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus and rhinovirus.
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Mycoplasma pneumonia is caused by bacteria called mycoplasma pneumoniae. It is a type of bacteria that often causes a mild infection of respiratory system. The symptoms include fever, chills, sore throat, diarrhea and rash. It usually affects people younger than age 40.
Diagnosis of pneumonia
For proper diagnosis, your doctor will review your medical history, perform a physical examination and run some tests. The test may include:
Chest X- ray
It takes pictures of the lungs, internal tissues and bones.
Arterial blood gas test
It measures the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in body.
Chest CT scan
This test takes detailed pictures of the structures in the chest. It is rarely done.
Pulse oximetry
An oximeter is a machine that measures the amount of oxygen in the blood.
Sputum samples
Sputum sample is collected and studied under the microscope. It detects whether the pneumonia is caused by a bacteria, a virus, or a fungus.
Treatment of pneumonia
Treatment depends on the cause of pneumonia. Most people can manage their symptom at home with medication. If your symptoms are severe you may need to go into the hospital. Common medications include:
Antibiotics
If pneumonia is caused by bacteria; your doctor will prescribe you antibiotics. It is important to take the full course of antibiotic as prescribed, even if you start to feel better. Stoppage may cause infection to come back. Antibiotics only act against bacteria; they do not work to treat viral pneumonia. Viral pneumonia usually goes away on its own. Your doctor may prescribe an anti-viral medicine to treat it.
Antifungal medication
Antifungal medications are given to fight fungal pneumonia.
Painkiller
Painkiller like paracetamol may help relieve pain and reduce fever.
Prevention
You can help prevent pneumonia by doing the following:
- Practice good hygiene habits. Wash your hands regularly and avoid contact with sick people.
- Practice a healthy lifestyle. Eat a balanced diet and drink lots of fluid.
- Always cover up your mouth while coughing and sneezing.
- Get plenty of rest and sleep to help your body recover.
- Get the pneumococcal vaccine- Pneumococcal pneumonia may be prevented with a vaccine in some cases. Two vaccines (Prevnar, Pneumovax) are available to prevent pneumonia from streptococcus pneumoniae.
Prevnar 13
It protects against 13 types of pneumococcal bacteria. Prevnar is usually recommended for children younger than 5 years. But now it is also recommended in adults up to the age of 65 years and older with certain health issues.
Pneumovax 23
It protects against 23 pneumococcal bacteria. It is indicated in adults 50 years of age or older and persons greater than or equal to 2 years of age who are at increased risk for pneumococcal disease.
DISCLAIMER
This web page provides general information and discussions about health, medicine and related subjects. The information and other content provided on this website, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment.
The content is for information purpose only and is not a medical advice. Qualified doctors have gathered information from reputable sources; however Credence Medicure Corporation is not responsible for errors or omissions in reporting or explanations. No individual should use the information, resources and tools contained herein to self diagnose or self treat any medical condition.
If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your health care provider or seek other professional medical treatment. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something that have read on this blog or in any linked materials. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately.
The opinions and views expressed on this blog and website have no relation to those of any academic, hospital, health practice or other institution. Credence Medicure Corporation gives no assurance or warranty regarding the accuracy, timeliness or applicability of the content.
