Osteoarthritis
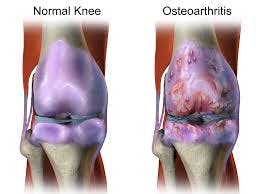
Osteoarthritis, also known as Degenerative joint disease is the most common type of arthritis that results from joint degeneration. It develops over time from normal wear and tear of the joint or from injuries. It is characterized by gradual loss of cartilage, which cushions the end of bones between joints and allows smooth joint movement. It most commonly affects the joints in hands, hip, spine, feet, and knees.
Osteoarthritis is more common in women than men. It occurs slowly and commonly occurs in middle age or late adulthood. It involves the entire joint including the ligaments, nearby muscles, and underlying bone. This leads to pain and stiffness that worsens over time.
Cause
Wear and tear can cause osteoarthritis when the cartilage that supports and cushions the joints of the spines, hand, knees, and hips wears away causing bones to rub against each other. Cartilage Wear and tear isn’t the only cause, other conditions that can result in Osteoarthritis are:
- Aging
- Injury
- Heredity
- Other Conditions – Osteoarthritis is the end result of variety of disorders. Certain conditions that promote osteoarthritis development include Diabetes, hyperthyroidism, obesity and acromegaly.
What are the risk factors for Osteoarthritis (OA)?
- Age: The risk of developing Osteoarthritis increases with age. It is the major risk factor for osteoarthritis.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis than men.
- Obesity: Overweight people bare more stress on the joint. The extra weight puts more strain on the joint.
- Genetics: There are chances of getting osteoarthritis if you have a family history.
- Sports: Athletes who sustain multiple joint injuries also can be affected. Some sports are more likely to lead to osteoarthritis.
- Previous joint injury
Symptoms
Symptoms vary from person to person. Onset of osteoarthritis is gradual, beginning with one or few joints. Osteoarthritis may affect any joint in the body. The most common symptoms of osteoarthritis include:
- Pain: Pain is the earliest symptoms of osteoarthritis. Without cartilage, bones rub against each other as the joints move and cause pain.
- Bone Spurs: Sometimes small bony extensions grow on the edges of osteoarthritic joints.
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Loss of range of motion
- Tenderness
- Cracking noise with joint movement
Diagnosis
For diagnosing osteoarthritis, your doctor may review the symptoms and examine your joints. Few tests like X-ray, MRI, and CT scan can be taken to determine the extent of joint damage.
Treatment
There is no cure for osteoarthritis, but there are many treatment options available to help manage pain. The goal of osteoarthritis treatment is early diagnosis, to reduce pain and improve function.
Medications
Pain and stiffness of osteoarthritis can be relieved with over-the-counter pain relievers. Acetaminophen is the over-the-counter drug that is commonly recommended for pain management. Other medications to control pain include NSAIDs such as aspirin, ibuprofen. NSAIDs may be used simultaneously with other analgesics to provide relief of symptoms. Some NSAIDs are available as cream, which has to be applied directly to the affected joint.
If over-the-counter drugs are ineffective then prescription medications are needed. In this case, doctor may recommend a strong anti inflammatory drug called corticosteroid which is injected directly into the joint.
Physical activity
Regular exercise strengthens the muscle and stimulates the cartilage growth. Ice or heat may need to be applied to the affected area for short periods. Some supportive devices like splints and braces can reduce joint stress, relieve pain and improve function and mobility.
Weight loss
A weight loss program may be recommended. Moderate weight loss often reduces pain. Losing weight reduces pressure on joints.
Surgery
Surgery should be recommended for those that have not responded to other therapies. Surgical options include Arthroscopy, Osteotomy, Chondroplasty, and Arthrodesis.
Diet
Vitamin D and Calcium are recommended. Dairy products are the best source of Calcium.
DISCLAIMER
This web page provides general information and discussions about health, medicine and related subjects. The information and other content provided on this website, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment.
The content is for information purpose only and is not a medical advice. Qualified doctors have gathered information from reputable sources; however Credence Medicure Corporation is not responsible for errors or omissions in reporting or explanations. No individual should use the information, resources and tools contained herein to self diagnose or self treat any medical condition.
If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your health care provider or seek other professional medical treatment. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something that have read on this blog or in any linked materials. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately.
The opinions and views expressed on this blog and website have no relation to those of any academic, hospital, health practice or other institution. Credence Medicure Corporation gives no assurance or warranty regarding the accuracy, timeliness or applicability of the content.